






































Trailer Industries(Customised Manufacturing)
Quicklime
 Quicklime (or calcium oxide or burnt lime) is obtained by calcining pure limestone at temperature above 9000C. This highly reactive product is essential to many industrial processes. Calcium oxide (CaO), commonly known as quicklime or burnt lime, is a widely used chemical compound. It is a white, caustic, alkaline, crystalline solid at room temperature. The broadly used term lime connotes calcium-containing inorganic materials, in which carbonates, oxides and hydroxides of calcium, silicon, magnesium, aluminium, and iron predominate.industrial applications include : Steel Making, FGD, Construction, Masonry & Mortars, Water Treatment, Chemical Processes, Mining Industry, sugar industry, Paper, Pulp and PCC, Remediation of Sludges and Wastes and Glass Manufacturing
Quicklime (or calcium oxide or burnt lime) is obtained by calcining pure limestone at temperature above 9000C. This highly reactive product is essential to many industrial processes. Calcium oxide (CaO), commonly known as quicklime or burnt lime, is a widely used chemical compound. It is a white, caustic, alkaline, crystalline solid at room temperature. The broadly used term lime connotes calcium-containing inorganic materials, in which carbonates, oxides and hydroxides of calcium, silicon, magnesium, aluminium, and iron predominate.industrial applications include : Steel Making, FGD, Construction, Masonry & Mortars, Water Treatment, Chemical Processes, Mining Industry, sugar industry, Paper, Pulp and PCC, Remediation of Sludges and Wastes and Glass Manufacturing
CaCO3(s) -> CaO(s) + CO2(g)
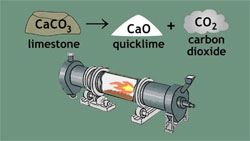 The quicklime is not stable and, when cooled, will spontaneously react with CO2 from the air until, after enough time, it will be completely converted back to calcium carbonate unless slaked with water to set as lime plaster or lime mortar.
The quicklime is not stable and, when cooled, will spontaneously react with CO2 from the air until, after enough time, it will be completely converted back to calcium carbonate unless slaked with water to set as lime plaster or lime mortar.
VIEW OUR PRODUCTS

Quicklime
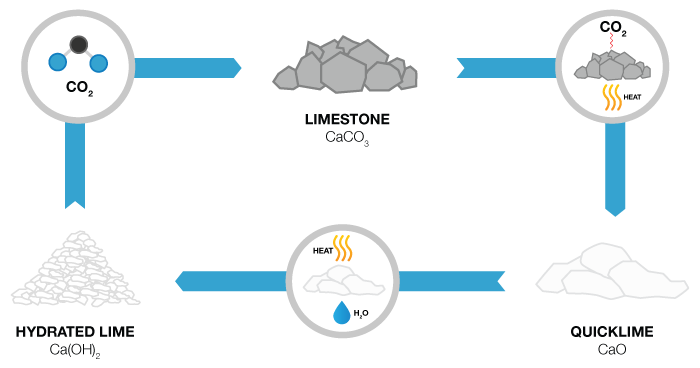
Calcium hydroxide (traditionally called slaked lime) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Ca(OH)2. It is a colorless crystal or white powder and is obtained when calcium oxide (called lime or quicklime) is mixed, or slaked with water. It has many names including hydrated lime, caustic lime, builders’ lime, slack lime, cal, or pickling lime. Calcium hydroxide is used in many applications, including food preparation. Limewater is the common name for a saturated solution of calcium hydroxide.industrial applications include : Sugar industry, Paint industry, steel industry, paper industry.

Quick Lime Powder
Quicklime (or calcium oxide or burnt lime) is obtained by calcining pure limestone at temperature above 9000C. This highly reactive product is essential to many industrial processes. Calcium oxide (CaO), commonly known as quicklime or burnt lime, is a widely used chemical compound. It is a white, caustic, alkaline, crystalline solid at room temperature. The broadly used term lime connotes calcium-containing inorganic materials, in which carbonates, oxides and hydroxides of calcium, silicon, magnesium, aluminium, and iron predominate.industrial applications include : Steel Making, FGD, Construction, Masonry & Mortars, Water Treatment, Chemical Processes, Mining Industry, sugar industry, Paper, Pulp and PCC, Remediation of Sludges and Wastes and Glass Manufacturing
CaCO3(s) -> CaO(s) + CO2(g)
 The quicklime is not stable and, when cooled, will spontaneously react with CO2 from the air until, after enough time, it will be completely converted back to calcium carbonate unless slaked with water to set as lime plaster or lime mortar.
The quicklime is not stable and, when cooled, will spontaneously react with CO2 from the air until, after enough time, it will be completely converted back to calcium carbonate unless slaked with water to set as lime plaster or lime mortar.

Hydrated Lime
Calcium hydroxide (traditionally called slaked lime) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Ca(OH)2. It is a colorless crystal or white powder and is obtained when calcium oxide (called lime or quicklime) is mixed, or slaked with water. It has many names including hydrated lime, caustic lime, builders’ lime, slack lime, cal, or pickling lime. Calcium hydroxide is used in many applications, including food preparation. Limewater is the common name for a saturated solution of calcium hydroxide.industrial applications include : Sugar industry, Paint industry, steel industry, paper industry.

Because of its low toxicity and the mildness of its basic properties, slaked lime is widely used in the food industry to:
make Chinese century eggs and many more.
clarify raw juice from sugarcane or sugar beets in the sugar industry, (see carbonatation)
process water for alcoholic beverages and soft drinks
pickle cucumbers and other foods
